MarkupText¶
限定名称: manim.mobject.text.text\_mobject.MarkupText
- class MarkupText(text, fill_opacity=1, stroke_width=0, color=None, font_size=48, line_spacing=-1, font='', slant='NORMAL', weight='NORMAL', justify=False, gradient=None, tab_width=4, height=None, width=None, should_center=True, disable_ligatures=False, warn_missing_font=True, **kwargs)[source]¶
基础:
SVGMobject使用 Pango 渲染显示(非 LaTeX)文本。
文本对象表现为给定文本中所有字符的类似
VGroup的可迭代对象。特别是,可以进行切片。什么是 PangoMarkup?
PangoMarkup 是一种类似 HTML 的小型标记语言,它帮助您在为文本片段着色或设置样式时避免使用“字符范围”。您可以将此语言与
MarkupText一起使用。标记字符串的一个简单示例如下:
<span foreground="blue" size="x-large">Blue text</span> is <i>cool</i>!"
并且可以与
MarkupText一起使用,如下所示:示例: MarkupExample ¶

from manim import * class MarkupExample(Scene): def construct(self): text = MarkupText('<span foreground="blue" size="x-large">Blue text</span> is <i>cool</i>!"') self.add(text)
class MarkupExample(Scene): def construct(self): text = MarkupText('Blue text is cool!"') self.add(text)一个更复杂的示例如下:
示例: MarkupElaborateExample ¶

from manim import * class MarkupElaborateExample(Scene): def construct(self): text = MarkupText( '<span foreground="purple">ا</span><span foreground="red">َ</span>' 'ل<span foreground="blue">ْ</span>ع<span foreground="red">َ</span>ر' '<span foreground="red">َ</span>ب<span foreground="red">ِ</span>ي' '<span foreground="green">ّ</span><span foreground="red">َ</span>ة' '<span foreground="blue">ُ</span>' ) self.add(text)
class MarkupElaborateExample(Scene): def construct(self): text = MarkupText( 'اَ' 'لْعَر' 'َبِي' 'َّة' 'ُ' ) self.add(text)PangoMarkup 还可以包含 XML 特性,例如数字字符实体,例如
©代表 © 也可以使用。最通用的标记标签是
<span>,然后还有一些便捷标签。以下是支持的标签列表:
<b>bold</b>,<i>italic</i>和<b><i>bold+italic</i></b><u>underline</u>和<s>strike through</s><tt>打字机字体</tt><big>更大字体</big>和<small>更小字体</small><sup>上标</sup>和<sub>下标</sub><span underline="double" underline_color="green">双下划线</span><span underline="error">错误下划线</span><span overline="single" overline_color="green">上划线</span><span strikethrough="true" strikethrough_color="red">删除线</span><span font_family="sans">临时改变字体</span><span foreground="red">临时改变颜色</span><span fgcolor="red">临时改变颜色</span><gradient from="YELLOW" to="RED">临时渐变</gradient>
对于
<span>标记,颜色可以指定为像#aabbcc这样的十六进制三元组,也可以是像AliceBlue这样的命名 CSS 颜色。<gradient>标签由 Manim 而非 Pango 处理,支持十六进制三元组或 Manim 常量,如RED或RED_A。 如果您想将 Manim 常量(如RED_A)与<span>一起使用,您需要使用 Python 的 f-字符串语法,如下所示:MarkupText(f'<span foreground="{RED_A}">here you go</span>')
如果您的文本包含连字,
MarkupText类在创建渐变时可能会错误地确定第一个和最后一个字母。这是因为fl是两个独立的字符,但可能被设置为一个单独的字形——一个连字。如果您的语言不依赖连字,请考虑将disable_ligatures设置为True。如果您必须使用连字,gradient标签支持一个可选属性offset,可用于补偿该错误。例如:
<gradient from="RED" to="YELLOW" offset="1">example</gradient>以便渐变提前一个字母开始<gradient from="RED" to="YELLOW" offset=",1">example</gradient>以便渐变提前一个字母结束<gradient from="RED" to="YELLOW" offset="2,1">example</gradient>以便渐变提前两个字母开始并提前一个字母结束
如果要着色的文本本身包含连字,则可能需要指定第二个偏移量。在使用 HTML 实体表示特殊字符时也可能发生同样的情况。
当
underline、overline或strikethrough与<gradient>标签一起使用时,您也需要使用偏移量,因为下划线是最终SVGMobject中的额外路径。请参阅以下示例。特殊字符转义:
>应该写为>,而<和&必须写为<和&。您可以在相应的文档页面找到有关 Pango 标记格式的更多信息:Pango Markup。请注意,并非所有功能都受此类的支持,并且上面提到的
<gradient>标签不受 Pango 支持。- 参数:
text (str) – 需要创建为 mobject 的文本。
fill_opacity (float) – 填充不透明度,1 表示不透明,0 表示透明。
stroke_width (float) – 描边宽度。
font_size (float) – 字体大小。
line_spacing (int) – 行间距。
font (str) – 整个文本的全局字体设置。支持局部覆盖。
slant (str) – 全局倾斜设置,例如 NORMAL 或 ITALIC。支持局部覆盖。
weight (str) – 全局字重设置,例如 NORMAL 或 BOLD。支持局部覆盖。
gradient (tuple) – 全局渐变设置。支持局部覆盖。
warn_missing_font (bool) – 如果为 True(默认),如果字体不存在于 manimpango.list_fonts() 返回的(区分大小写的)字体列表中,Manim 将发出警告。
color (ParsableManimColor | None)
justify (bool)
tab_width (int)
height (int)
width (int)
should_center (bool)
disable_ligatures (bool)
- 返回:
显示为类似
VGroup的 mobject 形式的文本。- 返回类型:
示例
示例: BasicMarkupExample ¶

from manim import * class BasicMarkupExample(Scene): def construct(self): text1 = MarkupText("<b>foo</b> <i>bar</i> <b><i>foobar</i></b>") text2 = MarkupText("<s>foo</s> <u>bar</u> <big>big</big> <small>small</small>") text3 = MarkupText("H<sub>2</sub>O and H<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup>") text4 = MarkupText("type <tt>help</tt> for help") text5 = MarkupText( '<span underline="double">foo</span> <span underline="error">bar</span>' ) group = VGroup(text1, text2, text3, text4, text5).arrange(DOWN) self.add(group)
class BasicMarkupExample(Scene): def construct(self): text1 = MarkupText("foo bar foobar") text2 = MarkupText("foobar big small") text3 = MarkupText("H2O and H3O+") text4 = MarkupText("type help for help") text5 = MarkupText( 'foo bar' ) group = VGroup(text1, text2, text3, text4, text5).arrange(DOWN) self.add(group)示例: ColorExample ¶

from manim import * class ColorExample(Scene): def construct(self): text1 = MarkupText( f'all in red <span fgcolor="{YELLOW}">except this</span>', color=RED ) text2 = MarkupText("nice gradient", gradient=(BLUE, GREEN)) text3 = MarkupText( 'nice <gradient from="RED" to="YELLOW">intermediate</gradient> gradient', gradient=(BLUE, GREEN), ) text4 = MarkupText( 'fl ligature <gradient from="RED" to="YELLOW">causing trouble</gradient> here' ) text5 = MarkupText( 'fl ligature <gradient from="RED" to="YELLOW" offset="1">defeated</gradient> with offset' ) text6 = MarkupText( 'fl ligature <gradient from="RED" to="YELLOW" offset="1">floating</gradient> inside' ) text7 = MarkupText( 'fl ligature <gradient from="RED" to="YELLOW" offset="1,1">floating</gradient> inside' ) group = VGroup(text1, text2, text3, text4, text5, text6, text7).arrange(DOWN) self.add(group)
class ColorExample(Scene): def construct(self): text1 = MarkupText( f'all in red except this', color=RED ) text2 = MarkupText("nice gradient", gradient=(BLUE, GREEN)) text3 = MarkupText( 'niceintermediate gradient', gradient=(BLUE, GREEN), ) text4 = MarkupText( 'fl ligaturecausing trouble here' ) text5 = MarkupText( 'fl ligaturedefeated with offset' ) text6 = MarkupText( 'fl ligaturefloating inside' ) text7 = MarkupText( 'fl ligaturefloating inside' ) group = VGroup(text1, text2, text3, text4, text5, text6, text7).arrange(DOWN) self.add(group)示例: UnderlineExample ¶
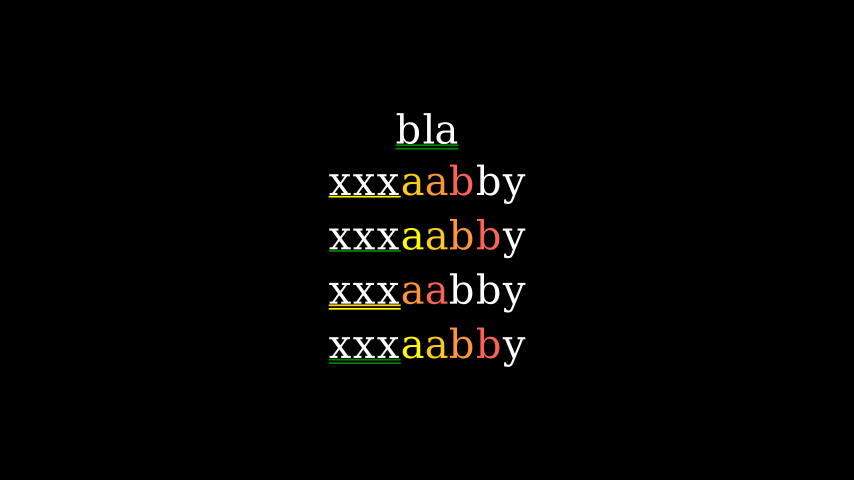
from manim import * class UnderlineExample(Scene): def construct(self): text1 = MarkupText( '<span underline="double" underline_color="green">bla</span>' ) text2 = MarkupText( '<span underline="single" underline_color="green">xxx</span><gradient from="#ffff00" to="RED">aabb</gradient>y' ) text3 = MarkupText( '<span underline="single" underline_color="green">xxx</span><gradient from="#ffff00" to="RED" offset="-1">aabb</gradient>y' ) text4 = MarkupText( '<span underline="double" underline_color="green">xxx</span><gradient from="#ffff00" to="RED">aabb</gradient>y' ) text5 = MarkupText( '<span underline="double" underline_color="green">xxx</span><gradient from="#ffff00" to="RED" offset="-2">aabb</gradient>y' ) group = VGroup(text1, text2, text3, text4, text5).arrange(DOWN) self.add(group)
class UnderlineExample(Scene): def construct(self): text1 = MarkupText( 'bla' ) text2 = MarkupText( 'xxxaabb y' ) text3 = MarkupText( 'xxxaabb y' ) text4 = MarkupText( 'xxxaabb y' ) text5 = MarkupText( 'xxxaabb y' ) group = VGroup(text1, text2, text3, text4, text5).arrange(DOWN) self.add(group)示例: FontExample ¶

from manim import * class FontExample(Scene): def construct(self): text1 = MarkupText( 'all in sans <span font_family="serif">except this</span>', font="sans" ) text2 = MarkupText( '<span font_family="serif">mixing</span> <span font_family="sans">fonts</span> <span font_family="monospace">is ugly</span>' ) text3 = MarkupText("special char > or >") text4 = MarkupText("special char < and &") group = VGroup(text1, text2, text3, text4).arrange(DOWN) self.add(group)
class FontExample(Scene): def construct(self): text1 = MarkupText( 'all in sans except this', font="sans" ) text2 = MarkupText( 'mixing fonts is ugly' ) text3 = MarkupText("special char > or >") text4 = MarkupText("special char < and &") group = VGroup(text1, text2, text3, text4).arrange(DOWN) self.add(group)示例: NewlineExample ¶
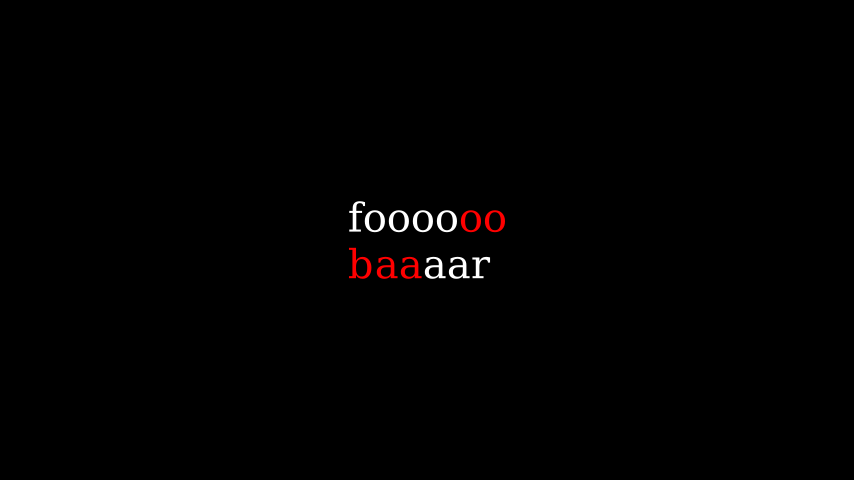
from manim import * class NewlineExample(Scene): def construct(self): text = MarkupText('foooo<span foreground="red">oo\nbaa</span>aar') self.add(text)
class NewlineExample(Scene): def construct(self): text = MarkupText('foooooo\nbaaaar') self.add(text)示例: NoLigaturesExample ¶

from manim import * class NoLigaturesExample(Scene): def construct(self): text1 = MarkupText('fl<gradient from="RED" to="GREEN">oat</gradient>ing') text2 = MarkupText('fl<gradient from="RED" to="GREEN">oat</gradient>ing', disable_ligatures=True) group = VGroup(text1, text2).arrange(DOWN) self.add(group)
class NoLigaturesExample(Scene): def construct(self): text1 = MarkupText('float ing') text2 = MarkupText('float ing', disable_ligatures=True) group = VGroup(text1, text2).arrange(DOWN) self.add(group)由于
MarkupText使用 Pango 渲染文本,因此可以轻松渲染非英文字符示例: MultiLanguage ¶

from manim import * class MultiLanguage(Scene): def construct(self): morning = MarkupText("வணக்கம்", font="sans-serif") japanese = MarkupText( '<span fgcolor="blue">日本</span>へようこそ' ) # works as in ``Text``. mess = MarkupText("Multi-Language", weight=BOLD) russ = MarkupText("Здравствуйте मस नम म ", font="sans-serif") hin = MarkupText("नमस्ते", font="sans-serif") chinese = MarkupText("臂猿「黛比」帶著孩子", font="sans-serif") group = VGroup(morning, japanese, mess, russ, hin, chinese).arrange(DOWN) self.add(group)
class MultiLanguage(Scene): def construct(self): morning = MarkupText("வணக்கம்", font="sans-serif") japanese = MarkupText( '日本へようこそ' ) # works as in ``Text``. mess = MarkupText("Multi-Language", weight=BOLD) russ = MarkupText("Здравствуйте मस नम म ", font="sans-serif") hin = MarkupText("नमस्ते", font="sans-serif") chinese = MarkupText("臂猿「黛比」帶著孩子", font="sans-serif") group = VGroup(morning, japanese, mess, russ, hin, chinese).arrange(DOWN) self.add(group)您可以通过传递
justify参数来对齐文本。示例: JustifyText ¶
from manim import * class JustifyText(Scene): def construct(self): ipsum_text = ( "Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit." "Praesent feugiat metus sit amet iaculis pulvinar. Nulla posuere " "quam a ex aliquam, eleifend consectetur tellus viverra. Aliquam " "fermentum interdum justo, nec rutrum elit pretium ac. Nam quis " "leo pulvinar, dignissim est at, venenatis nisi." ) justified_text = MarkupText(ipsum_text, justify=True).scale(0.4) not_justified_text = MarkupText(ipsum_text, justify=False).scale(0.4) just_title = Title("Justified") njust_title = Title("Not Justified") self.add(njust_title, not_justified_text) self.play( FadeOut(not_justified_text), FadeIn(justified_text), FadeOut(njust_title), FadeIn(just_title), ) self.wait(1)
class JustifyText(Scene): def construct(self): ipsum_text = ( "Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit." "Praesent feugiat metus sit amet iaculis pulvinar. Nulla posuere " "quam a ex aliquam, eleifend consectetur tellus viverra. Aliquam " "fermentum interdum justo, nec rutrum elit pretium ac. Nam quis " "leo pulvinar, dignissim est at, venenatis nisi." ) justified_text = MarkupText(ipsum_text, justify=True).scale(0.4) not_justified_text = MarkupText(ipsum_text, justify=False).scale(0.4) just_title = Title("Justified") njust_title = Title("Not Justified") self.add(njust_title, not_justified_text) self.play( FadeOut(not_justified_text), FadeIn(justified_text), FadeOut(njust_title), FadeIn(just_title), ) self.wait(1)测试
检查
MarkupText的创建是否正常工作>>> MarkupText('The horse does not eat cucumber salad.') MarkupText('The horse does not eat cucumber salad.')
方法
字体列表属性
animate (动画)用于动画化
self的任何方法的应用。animation_overrides (动画覆盖)颜色depth (深度)mobject 的深度。
fill_color (填充颜色)如果存在多种颜色(用于渐变),则返回第一种颜色
字体大小哈希种子代表生成的mobject点结果的唯一哈希值。
height (高度)mobject 的高度。
n_points_per_curve (每条曲线的点数)sheen_factor (光泽因子)stroke_color (描边颜色)width (宽度)mobject 的宽度。
- _extract_color_tags()[source]¶
用于确定字符串的哪些部分(如果有)应使用自定义颜色进行格式化。
移除
<color>标签,因为它不是 Pango 标记的一部分,会导致错误。注意:使用
<color>标签已被弃用。一旦旧语法被移除,此函数也将被移除。
- _extract_gradient_tags()[source]¶
用于确定字符串的哪些部分(如果有)应使用渐变进行格式化。
移除
<gradient>标签,因为它不是 Pango 标记的一部分,会导致错误。
- _original__init__(text, fill_opacity=1, stroke_width=0, color=None, font_size=48, line_spacing=-1, font='', slant='NORMAL', weight='NORMAL', justify=False, gradient=None, tab_width=4, height=None, width=None, should_center=True, disable_ligatures=False, warn_missing_font=True, **kwargs)¶
初始化自身。有关准确签名,请参阅 help(type(self))。
- 参数:
text (str)
fill_opacity (float)
stroke_width (浮点数)
color (ParsableManimColor | None)
font_size (float)
line_spacing (int)
font (str)
slant (str)
weight (str)
justify (bool)
gradient (tuple)
tab_width (int)
height (int)
width (int)
should_center (bool)
disable_ligatures (bool)
warn_missing_font (bool)
- 返回类型:
无
- _text2hash(color)[source]¶
为文件名生成
sha256哈希。- 参数:
color (ParsableManimColor)
- _text2svg(color)[source]¶
使用 Pango 将文本转换为 SVG。
- 参数:
color (ParsableManimColor | None)