布局函数¶
全名: manim.mobject.graph.LayoutFunction
- 类 LayoutFunction(*args, **kwargs)[源]¶
基类:
Protocol一个用于自动布局函数的协议,这些函数计算图的布局,供
change_layout()使用。注意
布局函数必须是纯函数,即它不能修改传递给它的图。
示例
以下是一个示例,它将节点按排序顺序排列在 n x m 网格中。
示例: 自定义布局示例 ¶
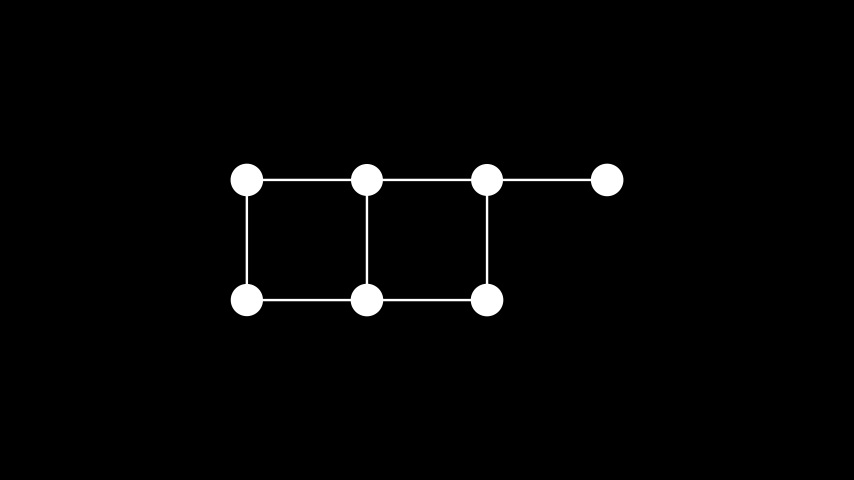
from manim import * class CustomLayoutExample(Scene): def construct(self): import numpy as np import networkx as nx # create custom layout def custom_layout( graph: nx.Graph, scale: float | tuple[float, float, float] = 2, n: int | None = None, *args: Any, **kwargs: Any, ): nodes = sorted(list(graph)) height = len(nodes) // n return { node: (scale * np.array([ (i % n) - (n-1)/2, -(i // n) + height/2, 0 ])) for i, node in enumerate(graph) } # draw graph n = 4 graph = Graph( [i for i in range(4 * 2 - 1)], [(0, 1), (0, 4), (1, 2), (1, 5), (2, 3), (2, 6), (4, 5), (5, 6)], labels=True, layout=custom_layout, layout_config={'n': n} ) self.add(graph)
class CustomLayoutExample(Scene): def construct(self): import numpy as np import networkx as nx # create custom layout def custom_layout( graph: nx.Graph, scale: float | tuple[float, float, float] = 2, n: int | None = None, *args: Any, **kwargs: Any, ): nodes = sorted(list(graph)) height = len(nodes) // n return { node: (scale * np.array([ (i % n) - (n-1)/2, -(i // n) + height/2, 0 ])) for i, node in enumerate(graph) } # draw graph n = 4 graph = Graph( [i for i in range(4 * 2 - 1)], [(0, 1), (0, 4), (1, 2), (1, 5), (2, 3), (2, 6), (4, 5), (5, 6)], labels=True, layout=custom_layout, layout_config={'n': n} ) self.add(graph)Manim 提供了多种自动布局,可以通过将其名称作为
layout参数传递给change_layout()来使用。或者,可以将自定义布局函数作为change_layout()的layout参数传递。此类函数必须遵循LayoutFunction协议。Manim 提供的
LayoutFunction类型如下所示圆形布局: 将顶点放置在一个圆上
示例: 圆形布局 ¶
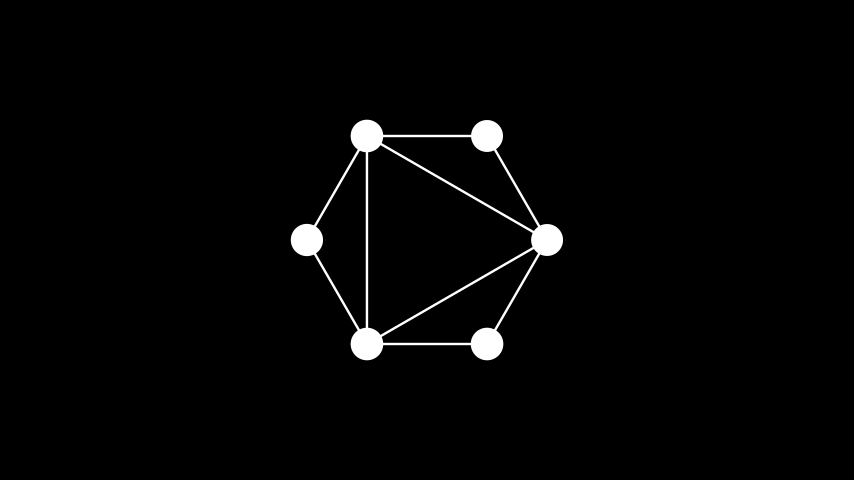
from manim import * class CircularLayout(Scene): def construct(self): graph = Graph( [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], [(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (4, 5), (5, 6), (6, 1), (5, 1), (1, 3), (3, 5)], layout="circular", labels=True ) self.add(graph)
class CircularLayout(Scene): def construct(self): graph = Graph( [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], [(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (4, 5), (5, 6), (6, 1), (5, 1), (1, 3), (3, 5)], layout="circular", labels=True ) self.add(graph)Kamada Kawai 布局: 尝试将顶点放置,使其之间的给定距离得以保持
示例: Kamada Kawai 布局 ¶
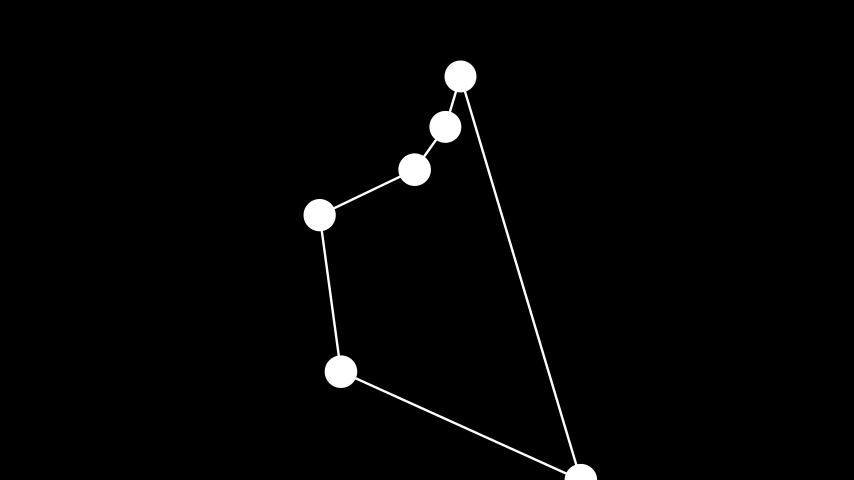
from manim import * class KamadaKawaiLayout(Scene): def construct(self): from collections import defaultdict distances: dict[int, dict[int, float]] = defaultdict(dict) # set desired distances distances[1][2] = 1 # distance between vertices 1 and 2 is 1 distances[2][3] = 1 # distance between vertices 2 and 3 is 1 distances[3][4] = 2 # etc distances[4][5] = 3 distances[5][6] = 5 distances[6][1] = 8 graph = Graph( [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], [(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (4, 5), (5, 6), (6, 1)], layout="kamada_kawai", layout_config={"dist": distances}, layout_scale=4, labels=True ) self.add(graph)
class KamadaKawaiLayout(Scene): def construct(self): from collections import defaultdict distances: dict[int, dict[int, float]] = defaultdict(dict) # set desired distances distances[1][2] = 1 # distance between vertices 1 and 2 is 1 distances[2][3] = 1 # distance between vertices 2 and 3 is 1 distances[3][4] = 2 # etc distances[4][5] = 3 distances[5][6] = 5 distances[6][1] = 8 graph = Graph( [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], [(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (4, 5), (5, 6), (6, 1)], layout="kamada_kawai", layout_config={"dist": distances}, layout_scale=4, labels=True ) self.add(graph)分部布局: 将顶点放置到不同的分区中
示例: 分部布局 ¶
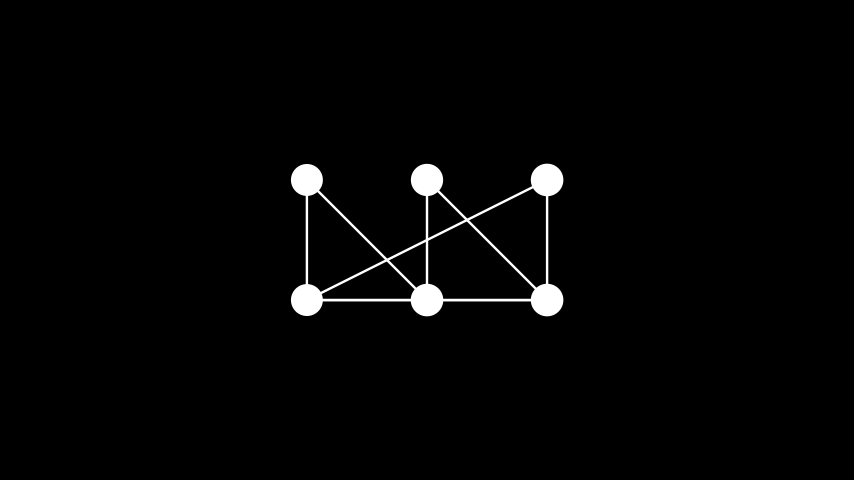
from manim import * class PartiteLayout(Scene): def construct(self): graph = Graph( [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], [(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (4, 5), (5, 6), (6, 1), (5, 1), (1, 3), (3, 5)], layout="partite", layout_config={"partitions": [[1,2],[3,4],[5,6]]}, labels=True ) self.add(graph)
class PartiteLayout(Scene): def construct(self): graph = Graph( [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], [(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (4, 5), (5, 6), (6, 1), (5, 1), (1, 3), (3, 5)], layout="partite", layout_config={"partitions": [[1,2],[3,4],[5,6]]}, labels=True ) self.add(graph)平面布局: 将顶点放置,使边不相交
示例: 平面布局 ¶
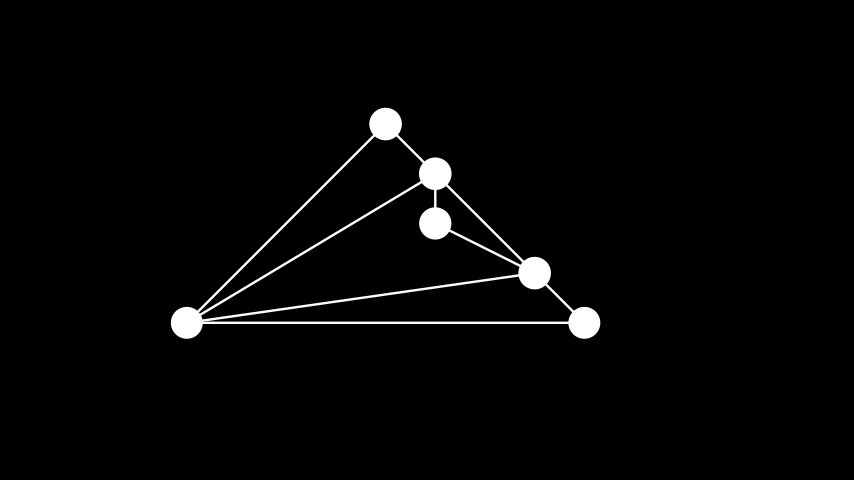
from manim import * class PlanarLayout(Scene): def construct(self): graph = Graph( [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], [(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (4, 5), (5, 6), (6, 1), (5, 1), (1, 3), (3, 5)], layout="planar", layout_scale=4, labels=True ) self.add(graph)
class PlanarLayout(Scene): def construct(self): graph = Graph( [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], [(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (4, 5), (5, 6), (6, 1), (5, 1), (1, 3), (3, 5)], layout="planar", layout_scale=4, labels=True ) self.add(graph)随机布局: 随机放置顶点
示例: 随机布局 ¶
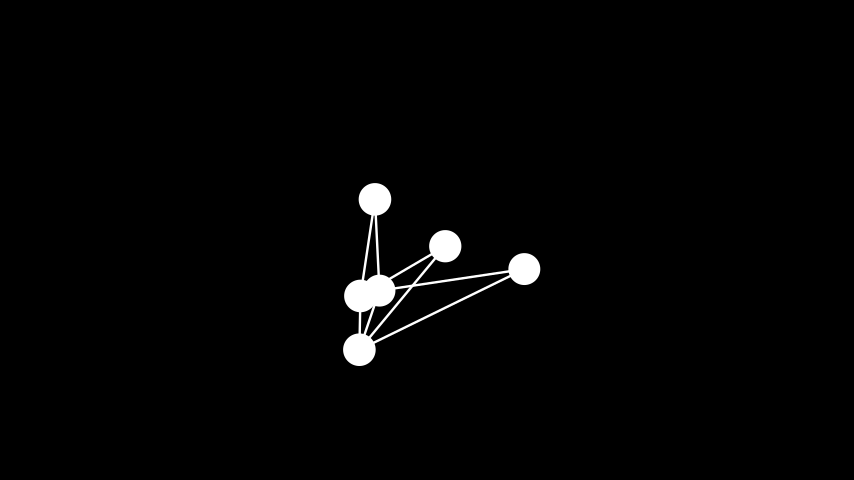
from manim import * class RandomLayout(Scene): def construct(self): graph = Graph( [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], [(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (4, 5), (5, 6), (6, 1), (5, 1), (1, 3), (3, 5)], layout="random", labels=True ) self.add(graph)
class RandomLayout(Scene): def construct(self): graph = Graph( [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], [(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (4, 5), (5, 6), (6, 1), (5, 1), (1, 3), (3, 5)], layout="random", labels=True ) self.add(graph)壳形布局: 将顶点放置在同心圆上
示例: 壳形布局 ¶
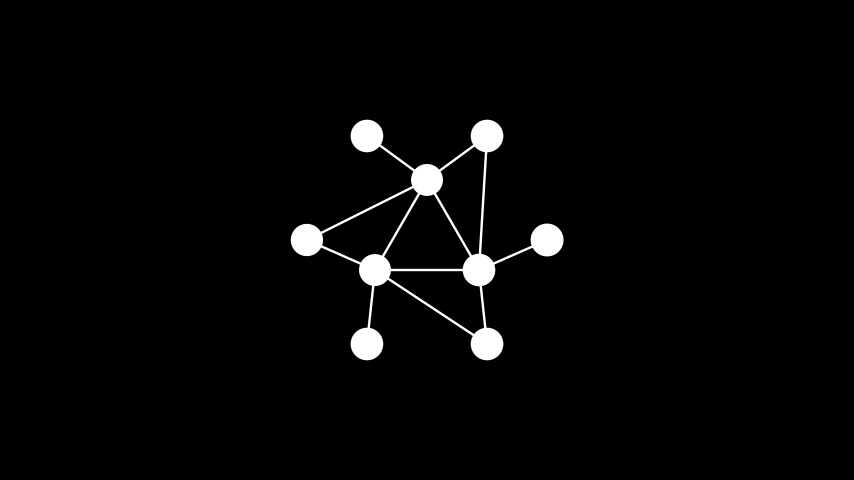
from manim import * class ShellLayout(Scene): def construct(self): nlist = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]] graph = Graph( [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9], [(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 1), (4, 1), (4, 2), (5, 2), (6, 2), (6, 3), (7, 3), (8, 3), (8, 1), (9, 1)], layout="shell", layout_config={"nlist": nlist}, labels=True ) self.add(graph)
class ShellLayout(Scene): def construct(self): nlist = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]] graph = Graph( [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9], [(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 1), (4, 1), (4, 2), (5, 2), (6, 2), (6, 3), (7, 3), (8, 3), (8, 1), (9, 1)], layout="shell", layout_config={"nlist": nlist}, labels=True ) self.add(graph)谱布局: 使用图拉普拉斯算子的特征向量放置顶点(聚类节点,这些节点是比率切割的近似值)
示例: 谱布局 ¶
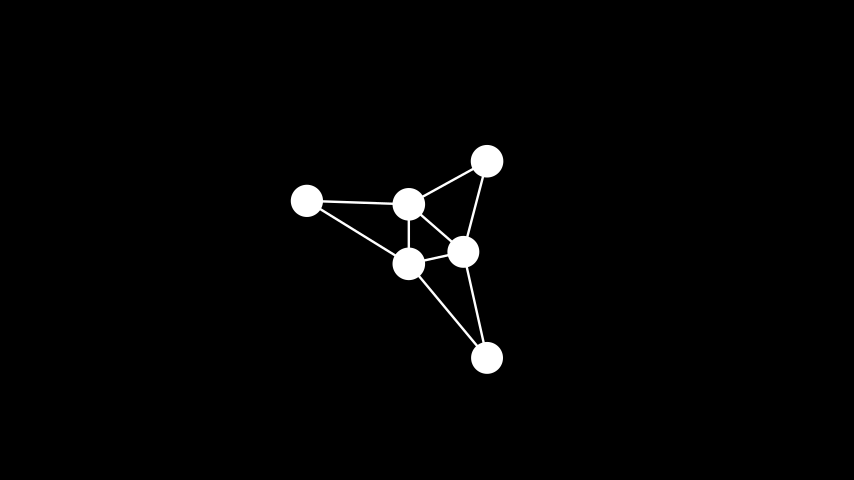
from manim import * class SpectralLayout(Scene): def construct(self): graph = Graph( [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], [(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (4, 5), (5, 6), (6, 1), (5, 1), (1, 3), (3, 5)], layout="spectral", labels=True ) self.add(graph)
class SpectralLayout(Scene): def construct(self): graph = Graph( [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], [(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (4, 5), (5, 6), (6, 1), (5, 1), (1, 3), (3, 5)], layout="spectral", labels=True ) self.add(graph)螺旋布局: 将顶点放置成螺旋状
示例: 螺旋布局 ¶
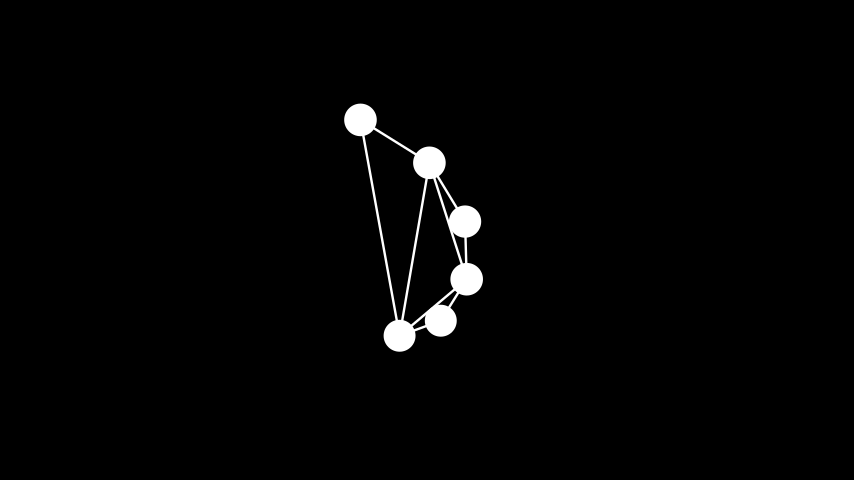
from manim import * class SpiralLayout(Scene): def construct(self): graph = Graph( [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], [(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (4, 5), (5, 6), (6, 1), (5, 1), (1, 3), (3, 5)], layout="spiral", labels=True ) self.add(graph)
class SpiralLayout(Scene): def construct(self): graph = Graph( [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], [(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (4, 5), (5, 6), (6, 1), (5, 1), (1, 3), (3, 5)], layout="spiral", labels=True ) self.add(graph)弹簧布局: 根据 Fruchterman-Reingold 力导向算法放置节点(尝试在最大化节点间距的同时最小化边长)
示例: 弹簧布局 ¶
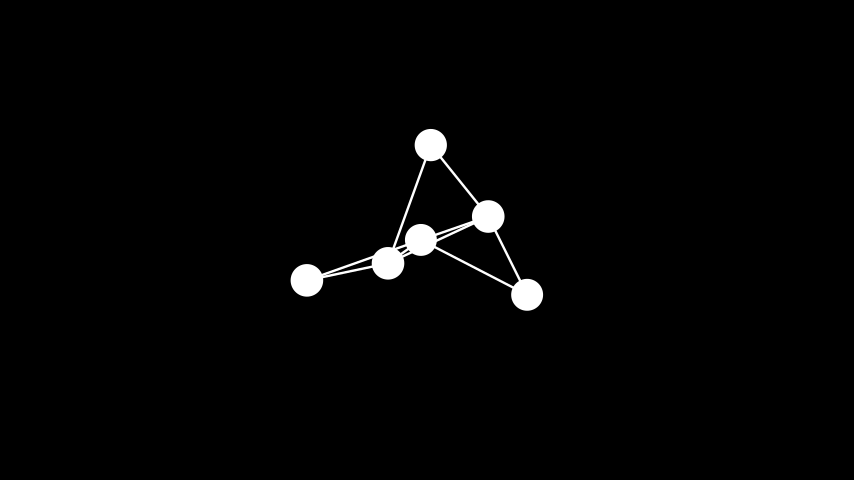
from manim import * class SpringLayout(Scene): def construct(self): graph = Graph( [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], [(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (4, 5), (5, 6), (6, 1), (5, 1), (1, 3), (3, 5)], layout="spring", labels=True ) self.add(graph)
class SpringLayout(Scene): def construct(self): graph = Graph( [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], [(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (4, 5), (5, 6), (6, 1), (5, 1), (1, 3), (3, 5)], layout="spring", labels=True ) self.add(graph)树形布局: 将顶点放置到具有根节点和分支的树中(只能用于合法树)
示例: 树形布局 ¶
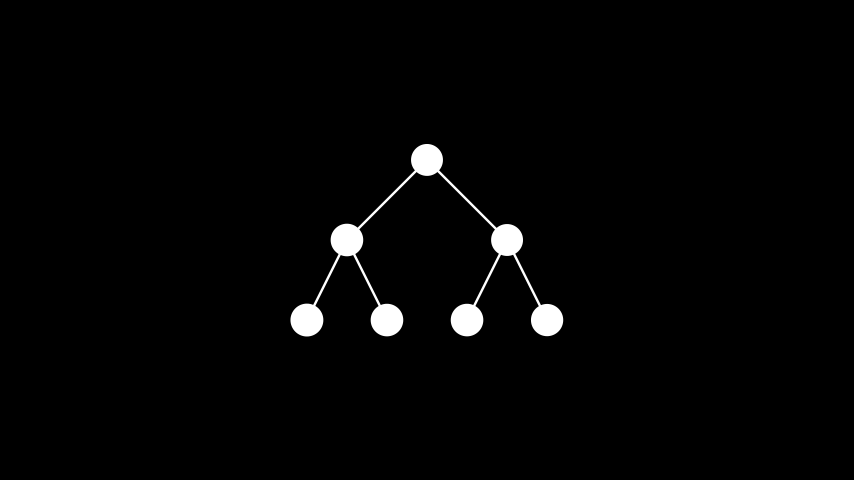
from manim import * class TreeLayout(Scene): def construct(self): graph = Graph( [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7], [(1, 2), (1, 3), (2, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6), (3, 7)], layout="tree", layout_config={"root_vertex": 1}, labels=True ) self.add(graph)
class TreeLayout(Scene): def construct(self): graph = Graph( [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7], [(1, 2), (1, 3), (2, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6), (3, 7)], layout="tree", layout_config={"root_vertex": 1}, labels=True ) self.add(graph)方法